INTRODUCTION
This is one of the vital aspects while planning personal finance — health insurance. In doing so, it acts as a fire-break against the unaffordable expenses of healthcare — by giving everyone and their family affordable access to necessary health services without financial ruin. This guide provides an introduction to health insurance, the terms you need to know and different kinds of plans that are available as well as how to find the right plan for your needs.
What is Health Insurance?
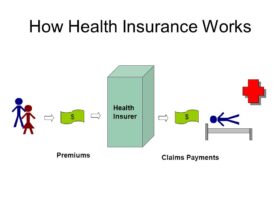
Health insurance is an insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses, spreading the risk over numerous persons. For example, hospital stays, doctor visits medications and other healthcare services can get costly. Health insurance, simply put, is the coverage of medical costs for individuals in order to prevent them from paying large sums when bills need covering.
Key Terms in Health Insurance
It can be a difficult task to understand health insurance as there are many terms that one needs to grasp. These are some of the most common ones:
Premium: How much you offer to keep your health insurance plan, typically each month.
Deductible : the amount you must pay each year for most covered services DESCRIPTION OUT-OF-NETWORK (if Applicable) 2 DESCRIPTION IN NETWORK Copayments Most copay plans does not include a deductible or coinsurance, but obviously that means higher monthly premiums BCBSNC.BLUCCI.POL(BCB7 BPDP).
Copayment (copay): A fixed amount for a service you pay after meeting your deductible, such as an office visit.
Coinsurance: The amount (usually a percentage) of the cost for medical services that you are required to pay. For example, you might have a 20% coinsurance which means that you would pay for the medical care and your insurance company would cover the rest.
Out-of-Pocket Maximum — the most you have to pay for covered services in a plan year.
Health Insurance Plan options
While there are different types of health insurance plans, each comes with its own pros and cons. Being aware of these can assist you in selecting a plan that meets your healthcare requirements and is within your spending limit.
1. HMO — Health Maintenance Organization Plans
HMO plans: HMO members must designate a primary care physician (PCP) and get referrals from that PCP to see specialists. While these plans usually have a lower premium and out-of-pocket expense, they can limit the choice of healthcare provider.
2. PPO — Preferred Provider Organization Plans
PPO plans PPO, or Preferred Provider Organization is a more flexible plan that allows you to visit any doctor without needing one referral. These typically have higher premiums but also encompass a larger network of healthcare providers.
3. 3) Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) Plans
EPO plans are a hybrid of HMO and PPO. While they allow some level of self-referral for physicians, the coverage is restricted to doctors and hospitals within their network.
4. Point of Service (POS) Plans
POS plans are like HMOs, where you get referrals to see specialists from the primary care physician chosen by a member of POS. On the other hand, they provide options for more expensive care from providers out of their network.
The trick to Landing the perfect Living Insurance Package deal
When choosing a plan, there are many factors that need to be considered in order for it to fit your needs and budget.
1. How to Assess Your Healthcare Needs
So be sure to think about your individual health, any underlying chronic conditions and the type of medical care you may expect. An HMO plan may be more cost-effective if you have only one primary care physician that you like to use, although a PPO might provide greater access depending on how often (if at all) you see specialists.
2. Cost Comparison: Premiums, Deductibles and Out-of-Pocket Maximums
Don’t just think about the premium cost per month. They do this by way of increased deductibles and out-of-pocket costs on lower-premium plans. Know what you may have to pay over the course of a year, especially in case an unexpected health issue arises.
3. Verify the Provider Network
Make sure the physicians, hospitals and specialists you prefer are in the plan network. The expense difference can be huge, being you on your own with a nonplan would either pay way more for an out-of-network service or just have the cost of said type of care not covered at all in some cases.
4. Know the Coverage and Benefits
Examine the nitty-gritty coverage details of your plan, including preventive services and emergency care, prescription drugs and mental health services. Check that the services most likely to use are specified in your plan.
Why Preventive Care Matters
A key part of health coverage is that it typically pays for treatment after you get sick, say heart surgery or a pacemaker to maintain an irregular heartbeat.
Another: preventive services with no extra charge to the cologne.
Preventive care: A benefit designed to pay for annual check-ups, vaccinations and screenings as well as any other services that can detect potential health problems before they become more serious or complicated. If you use these services, it may save your health and prevent greater ill-health in the future.
Health Insurance and Financial Protection
The price of the smallest health crisis without insurance can be crippling. Health insurance offers a defense against high medical bills by helping to pay those that would otherwise be your financial downfall and risk sending you spiraling into massive amounts of debt as well.
Conclusion: Planning your Decision
Health insurance can be confusing and choosing the best plan for yourself or your family may come as a challenge, but with just minimal knowledge on how everything works plus properly identifying what you would need will make sure that you are paying the right thing to save money when using it. Make sure to always compare plans, read the fine print and ask questions before choosing which plan is best for you and your health long term.
The purpose of getting health insurance is not just settlement of medical bills off us; it provides quality care and secures one against un unforeseeable expenditure incurred due to poor health. You should be able to make a decision based on being well informed and active in learning when it comes down to what would work best for your particular situation.


















Leave a Reply